Our energy regulatory lawyers have the expertise and in-depth understanding of the federal and state regulatory frameworks to address the many issues that confront regulated utilities, entities acquiring or selling energy generation facilities, and other parties subject to federal or state energy regulation, including ratemaking, purchase and sale and financing transactions, wholesale market participation and rules, compliance and investigations. At Pierce Atwood, our clients benefit from knowing that within a single law firm they have access to a team of accomplished energy lawyers to help them obtain the requisite federal and state regulatory approvals, navigate and comply with applicable federal and state regulations, and assess the impacts and risks of federal and state regulatory and policy developments.
Pierce Atwood offers a deep bench of attorneys who have served in senior policy positions at state and federal regulatory agencies. Our energy attorneys regularly practice before federal agencies, including the Federal Energy Regulatory Commission (FERC), U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC), Securities and Exchange Commission and U.S. Patent & Trademark Office. We also have extensive experience before numerous state regulatory agencies, including California, Connecticut, District of Columbia, Georgia, Maine, Maryland, Massachusetts, Michigan, New Hampshire, New Jersey, New York, Illinois, Pennsylvania, Rhode Island, Texas, Vermont, Virginia and Wisconsin. Several of our energy attorneys have previously served as staff to state and federal energy regulatory agencies and have a unique insight into how regulators approach various issues.
Ratemaking
Pierce Atwood’s energy attorneys have significant experience representing utilities and other interested parties in ratemaking proceedings before state and federal regulators. This experience includes all aspects of traditional cost of service ratemaking and rate design as well as performance-based or alternative ratemaking mechanisms, including rate adjustment indices, capital trackers, earning sharing, and service quality incentives and penalties. Our attorneys are knowledgeable and experienced in litigating rate proceedings through discovery and contested hearings or negotiating compromise solutions through the settlement process that benefit our clients.
Utility Mergers & Regulated Transactions
Pierce Atwood’s energy attorneys have significant experience representing utilities and other parties in obtaining necessary regulatory approvals for energy transactions, including federal and state approvals for utility mergers and purchase and sale transactions, affiliated transactions, and state-led energy procurements. Our attorneys have successfully negotiated fuel supply, transportation, and interconnection agreements for natural gas, biomass, LNG, and other fuels; interconnection agreements with electric transmission utilities; and power purchase agreements and other off-take contracts for the output of renewable and conventional fuel generation plants, and have obtained the necessary regulatory approvals for such agreements. In addition, we have substantial experience in obtaining approvals, exemptions and waivers under Public Utility Regulatory Policies Act of 1978, as amended (PURPA) and the Federal Power Act; in obtaining certificates under the Natural Gas Act for gas pipeline and storage facilities; in guiding developers of crude oil pipelines through the open season, declaratory order, and tariff processes; and in complying with state and federal gas and power marketing regulations. We pride ourselves in our ability to assist our clients in structuring their transactions to exempt them from or minimize the impacts of FERC and state jurisdiction.
Wholesale Market Rules
Pierce Atwood energy attorneys also have extensive experience working in and with FERC, Independent System Operators (ISOs) and Regional Transmission Organizations (RTOs) on market-based authorizations for wholesale sales of electric energy, capacity, and ancillary services; arrangements and agreements for new power generators to participate in the organized markets; and for the sale and acquisition of facilities. Our attorneys were at the forefront of the development of FERC’s rules and policies regarding (i) natural gas pipeline capacity release and open access transportation, as well as more recent regulations granting exemptions for shippers utilizing asset management arrangements, and in obtaining individual waivers from FERC for specific transportation transactions, and (ii) the participation of energy storage facilities in the organized ISO energy, ancillary services and capacity markets. Pierce Atwood attorneys regularly advise clients regarding market rules governing selling and trading in the PJM, ISO-New England, NYISO, California ISO, MISO and ERCOT regional markets.
Impacting Policies & Regulations
Energy projects typically involve important federal and state regulatory policy issues, contracts with regional electric or natural gas utilities, and dealing with ISOs. Pierce Atwood has a long and distinguished history of representing clients before state and federal energy regulators and helping to shape relevant energy policies. We regularly partner with our clients to collaborate with similarly situated companies to shape policies and regulations that support the advancement of renewable energy and the development of appropriate market rules.
Pierce Atwood represents energy clients in rulemaking proceedings before local, state, and federal agencies regarding all policy issues which would affect the development of electric power projects, electric transmission projects, and natural gas and oil pipelines and shippers. Our firm also has an experienced Governmental Relations team that assists our clients shape energy policy before State legislatures and federal and state agencies, including FERC and the U.S. Department of Energy. Learn more about our Government Relations Practice.
Regulatory Compliance & Investigations
Given our experience practicing before numerous federal and state energy regulators and understanding of the applicable laws and regulations, our energy attorneys also regularly advise on regulatory compliance matters. We conduct compliance training for electric and natural gas clients and, when necessary, represent clients in administrative investigations, show cause proceedings, management audits and prudency reviews.
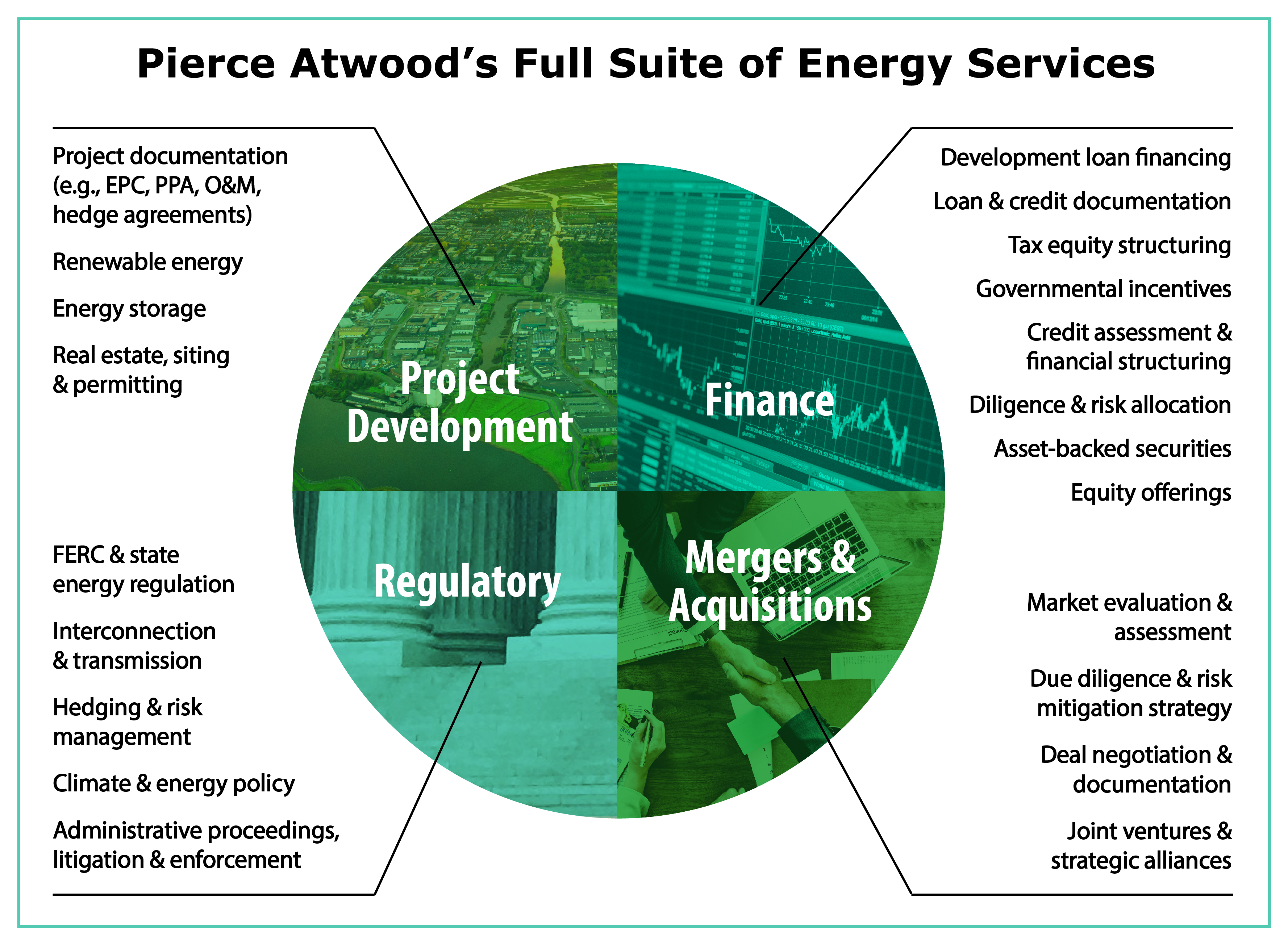
 Pierce Atwood has substantial experience negotiating the full array of agreements that are essential to a project’s success, and offers a deep bench of former regulators and private equity participants with deep insight into the regulatory approval and financing process– including the Chair of Federal Energy Regulatory Commission’s (FERC) Cogeneration and Small Power Production Task Force, Chief of Staff and General Counsel of the Massachusetts Department of Public Utilities (DPU), FERC’s Supervisory Attorney for Gas & Oil Litigation, FERC Commissioner Assistants, state public service commission attorneys, and board members of solar energy and biofuels companies.
Pierce Atwood has substantial experience negotiating the full array of agreements that are essential to a project’s success, and offers a deep bench of former regulators and private equity participants with deep insight into the regulatory approval and financing process– including the Chair of Federal Energy Regulatory Commission’s (FERC) Cogeneration and Small Power Production Task Force, Chief of Staff and General Counsel of the Massachusetts Department of Public Utilities (DPU), FERC’s Supervisory Attorney for Gas & Oil Litigation, FERC Commissioner Assistants, state public service commission attorneys, and board members of solar energy and biofuels companies.